Servers-Disk Server,File Server,Print Server,Communication Server, Application Server.
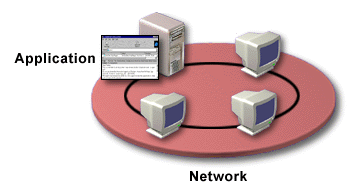



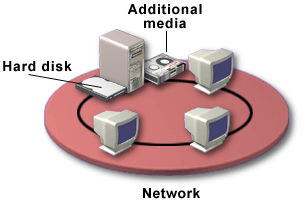
In a network, servers need to perform a number of tasks, such as storing data, creating files, and accessing applications. A large network supports dedicated servers for performing specific tasks. The following types of servers are mainly used in a large network.
1.disk server
2.file server
3.print server
4.communication server
5.application server
A disk server shares a hard disk in a network. It is primarily used for storing data in a network. Therefore, in addition to local storage, a client machine has access to some disk space on a disk server. The disk space can be used for taking backups. In addition to hard disk, a disk server can provide storage space by accommodating different data storage media, such as CDs, jazz, zip, cartridge tapes, etc. Clients can choose to store their data on any of these media.
File server provides a central storage mechanism for files. This enables users to store their files in one central location. When a user makes a request for a specific file, the file server sends the file to the user. File servers enable users to create, read, modify, and delete shared files.
A print server makes a printer available to network clients. Since a single printer can be made available to all the clients, clients do not need individual printers
In your network, you might require your microcomputers to communicate with mainframe computers. However, mainframe computers do not run on the same operating systems as microcomputers. In such a situation, a communication server enables the microcomputers to communicate with a mainframe computer. Communication servers typically handle the data flow, e-mail messages, and fax traffic within a network, and with other networks.
An application server enables clients to access software applications that reside on a shared computer. When a user makes a request to the application server, the database stays on the server and only the result of the request is sent to the computer making the request.